8 Industrial relations changes requiring actions by employers
There have been a number of recent significant changes in the area of industrial relations as a result of the Fair Work Legislation Amendment (Secure Jobs, Better Pay) Act 2022, and the Fair Work Amendment (Paid Family and Domestic Violence Leave) Act 2022.
Some of the main changes which will affect all businesses and require action include:
1. Proactive Duty on Employers to eliminate discriminatory conduct in workplaces
Employers, regardless of size or industry, now have a positive duty to take reasonable and proportionate measures to prevent, as far as possible, certain discriminatory conduct occurring in their workplaces, including:
- discrimination on the ground of a person’s sex;
- harassment (including sexual harassment);
- hostile workplace environments; and
- acts of victimisation that relate to complaints, proceedings or allegations of the above.
The positive duty was a key recommendation of the Australian Human Rights Commission (AHRC) landmark Respect@Work Report, led by Sex Discrimination Commissioner Kate Jenkins, published in March 2020, which found that there were still high levels of discrimination and underreporting of incidents in the workplace.
The AHRC will have the right to initiate an inquiry into an employer’s compliance and enter into enforceable undertakings if they find an employer remains non-compliant.
Businesses will have 12 months to understand their new obligations and implement any necessary changes before compliance and enforcement commences in December 2023.
2. Additional protection against Sexual Harassment
There has been an amendment to the Fair Work Act to protect workers, prospective workers and persons conducting or undertaking a business by prohibiting sexual harassment, effective from 6 March 2023.
This amendment established a new dispute resolution process, allowing the Fair Work Commission (the Commission) to deal with disputes and if not resolved by conciliation or mediation, and the parties agree, the Commission can settle the dispute and make orders, including for compensation.
Workers now have several avenues to pursue disputes in relation to sexual harassment: the Fair Work Commission, the Australian Human Rights Commission and Anti-Discrimination Board in their State or Territory.
We recommend implementing an action plan to address points 1 and 2 above to ensure your business is meeting its new legal obligations. Our team at Allan Hall HR is across the legislation and can effectively and efficiently guide you in creating an action plan for your business. Please contact our team on 1300 675 393 or at [email protected] if you would like our assistance.
3. Family and Domestic Violence Leave
From 1 February 2023, all employees (including part-time and casuals) will be able to access 10 days’ paid family and domestic violence leave in each 12-month period.
To access this paid leave, employees will need to show evidence that they require the leave to do something to deal with the impact of family and domestic violence and it’s not practical for them to do so during their work hours.
There are also important implications for payroll to consider, including the recording of leave on payslips, attendance platforms, email and text trails.
If you would like more information on this leave and its payroll implementation please refer to our Family and Domestic Violence Leave article or contact us on 1300 675 393 or at [email protected].
4. Limiting the use of fixed term contracts for employees
There has been an amendment to the Fair Work Act to limit the use of Fixed term contracts beyond two years (including renewals) or two consecutive contracts – whichever is shorter. Employers will also be required to provide a Fixed Term Contract Information Statement to all employees entering a fixed term contract. This amendment takes effect as of 6 December 2023.
Exceptions to this rule include; performing a discrete task for a fixed period, apprentices and trainees, temporarily replacing others on long leave e.g. workers compensation and where earnings are above the high income threshold.
Where a fixed term contract is made in breach of the new provision, the contract will remain valid, but the employee will be considered a permanent employee. This means they will be entitled to:
- notice of termination and redundancy payments calculated from the start of the employment relationship, and
- access to unfair dismissal proceedings.
Employers who breach the contract limitation or do not provide a Fixed Term Information Statement may be subject to civil penalties.
If you have employees who will, as at 6 December 2023, have been on a fixed term contract of more than 2 years’ duration or more than one fixed term contract which would add up, to or allows for an extension to, more than 2 years, you will need to review the arrangements. Allan Hall HR can help in reviewing old contracts and the creation of new ones, contact us on 1300 675 393 or at [email protected].
5. Prohibiting pay secrecy clauses
Employees will have a right to disclose, or not disclose, their remuneration as of 7 December 2022.
After a six-month transitional period, employers who continue to include pay secrecy terms in new written agreements and contracts of employment will have breached this prohibition and could be liable to a penalty.
All written agreements with employees need to be reviewed to ensure there is no clause prohibiting them from disclosing their remuneration.
6. Right to request flexible working arrangements
The circumstances in which employees can request a flexible working arrangement have expanded. This provision extends to employees who are pregnant and situations where an employee, or member of their immediate family or household, experiences family and domestic violence. This amendment takes effect as of 6 June 2023.
Employers are obligated to discuss any request for a flexible working arrangement with the employee. If the employer refuses the request, they will need to provide reasons in writing.
The threshold of “reasonable business grounds” for refusal of any request has not changed, however, the legislation provides increased access to dispute resolution for employees through the Fair Work Commission if disputes about flexible working arrangements cannot be resolved at the workplace.
Managers need to ensure that they discuss any request for flexible working arrangements with the employee and that any refusal is in writing and based on reasonable business grounds. If you would like additional guidance on when you are obligated to approve flexible work arrangements, contact the friendly team at Allan Hall HR for guidance on 1300 675 393 or at [email protected].
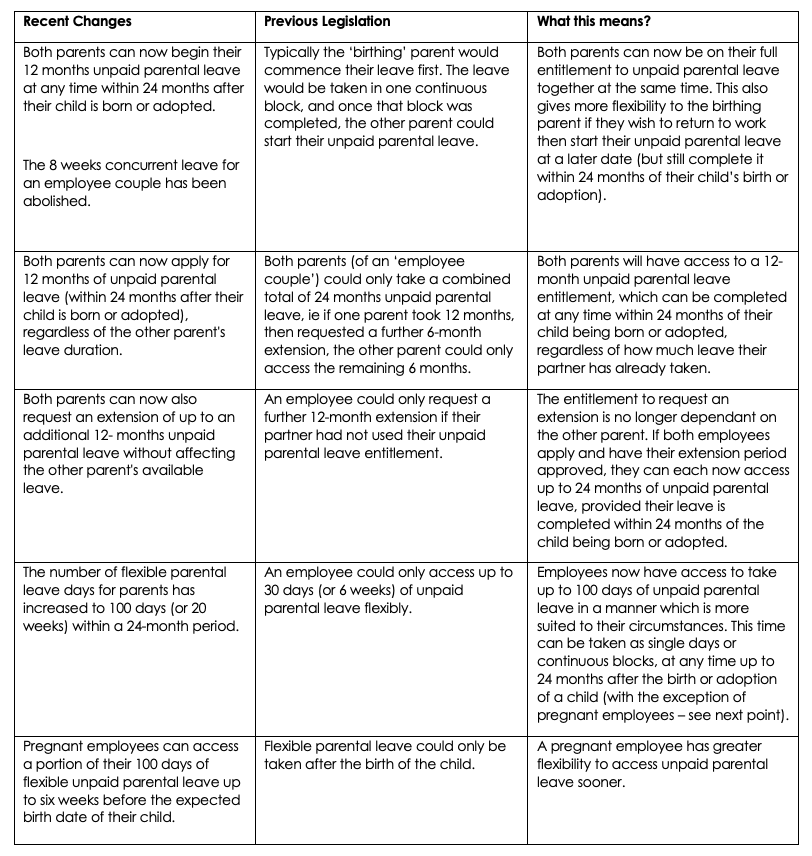
7. Unpaid Parental Leave
Eligible employees will be entitled to an additional 12 months’ unpaid parental leave up to 24 months in total, unless their partner has already taken 12 months from 6 June 2023.
When an eligible employee makes a request for an extension of unpaid parental leave, their employer has an obligation to discuss the request with them. If this request is refused, reasons must be provided to the employee in writing.
If disputes cannot be solved at the workplace level, they can be escalated through conciliation or mediation.
Any request for an extension of parental leave should be discussed with the employee. Any refusal must be in writing and based on reasonable business grounds.
8. Enterprise Bargaining and Enterprise Agreements
The Fair Work Act has been amended to include new enterprise agreement and bargaining laws which took effect from 7 December 2022. In summary:
- Changes have been introduced to simplify the bargaining process including reducing technical procedural steps prior to an agreement being approved.
- The “Better Off Overall Test” (BOOT) has been modified and the Commission will now undertake a ‘global assessment’ and take into account parties’ views to determine whether the agreement passes the BOOT.
- The process for terminating an enterprise agreement has changed and it is now more difficult for employers to unilaterally terminate an enterprise agreement after its nominal expiry date.
- Supported bargaining has been broadened and workers across multiple workplaces in a common sector will be able to bargain on a collective basis if they are ‘reasonably comparable’ in terms of the industry they operate within, their size, geographical location, business activities and operations.
- Certain workplace agreements (called ‘zombie agreements’) which were made before the Fair Work Act 2009 (Cth) fully commenced and that continue to operate (e.g. collective agreements, individual transitional employment agreements (or ITEAs), Australian Workplace Agreement (or AWAs), Division 2B State employment agreements, enterprise agreements made between 1 July and 31 December 2009) will automatically terminate on 7 December 2023 unless the employer applies for, and is granted, an extension. Employers who are covered by a ‘zombie agreement’ must also give each employee who is covered by their zombie agreement a written notice on or before 6 June 2023 advising the employee that:
- the employee is covered by a zombie agreement; and
- the zombie agreement will terminate on 7 December 2023 unless an extension request is made; and
- the sunsetting process commenced on 7 December 2022.
Need assistance? Please contact the team at Allan Hall HR on 1300 675 393 or at [email protected] should you require assistance with actioning any of these IR changes to ensure your business is compliant.